Four Redis Use Cases Outside of Caching
I use Redis for caching. I learned about some other neat use cases after watching ByteByteGo’s Redis video.
I decided to document these other use cases so that I could quickly refer back to them in the future.
Let’s First Level Set on What Redis Is
Redis is an in-memory date structure store that is most commonly used as a cache.
Supported Data Structures
Supports
- Strings
- Hashes
- Lists
- Sets
- Sorted Sets

Why use a Redis Cluster
At scale, the cache is distributed among a cluster of redis servers.
Redis Provides Persistence Options, but Using a Backup is Preferred in Production
Redis provides persistence options like snapshots and Append-Only File (AOF).
This allows…data to be saved to disk and reloaded into memory in the event of a restart.
…these options often take too long to load on restart to be practical
In production, replication is used instead. In this case, data is replicated to a backup instance.
In the event of a crash of the main instance, the backup is quickly promoted to take over the traffic.
Four Other Use Cases for Redis
Session Store
When a user logs in to a web application, the session data is stored in Redis along with a unique session ID that is returned to the client as a cookie.
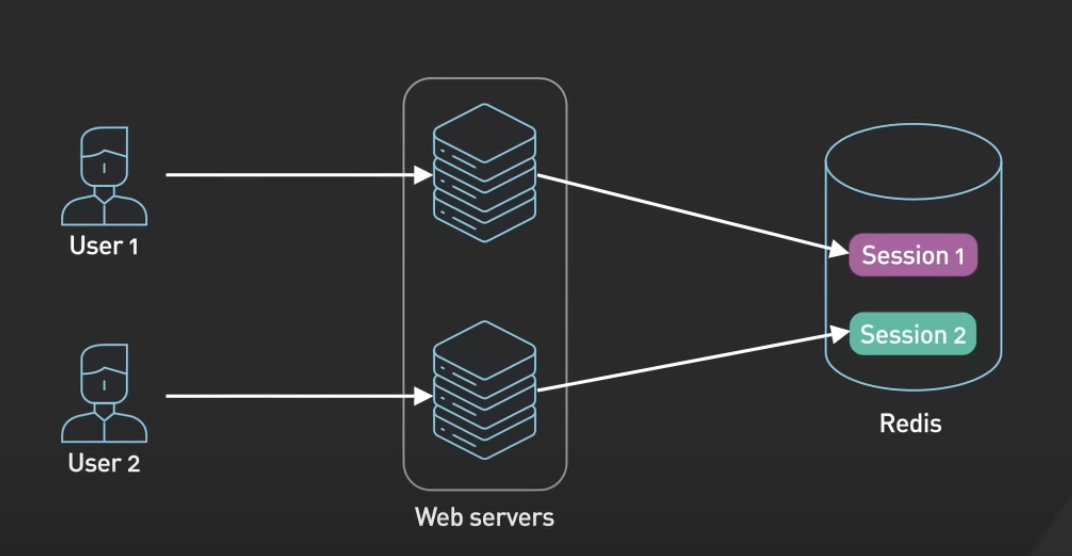
When the user makes a request to the application, the session ID is included in the request and the stateless web server retrieves the session data from Redis using the ID.
Distributed Lock
Distributed locks are used when multiple nodes in an application need to coordinate access to some shared resource.
Redis is used as a distributed lock with its atomic commands like SETNX (SET if Not eXists)
It allows a caller to set a key only if it does not already exist.
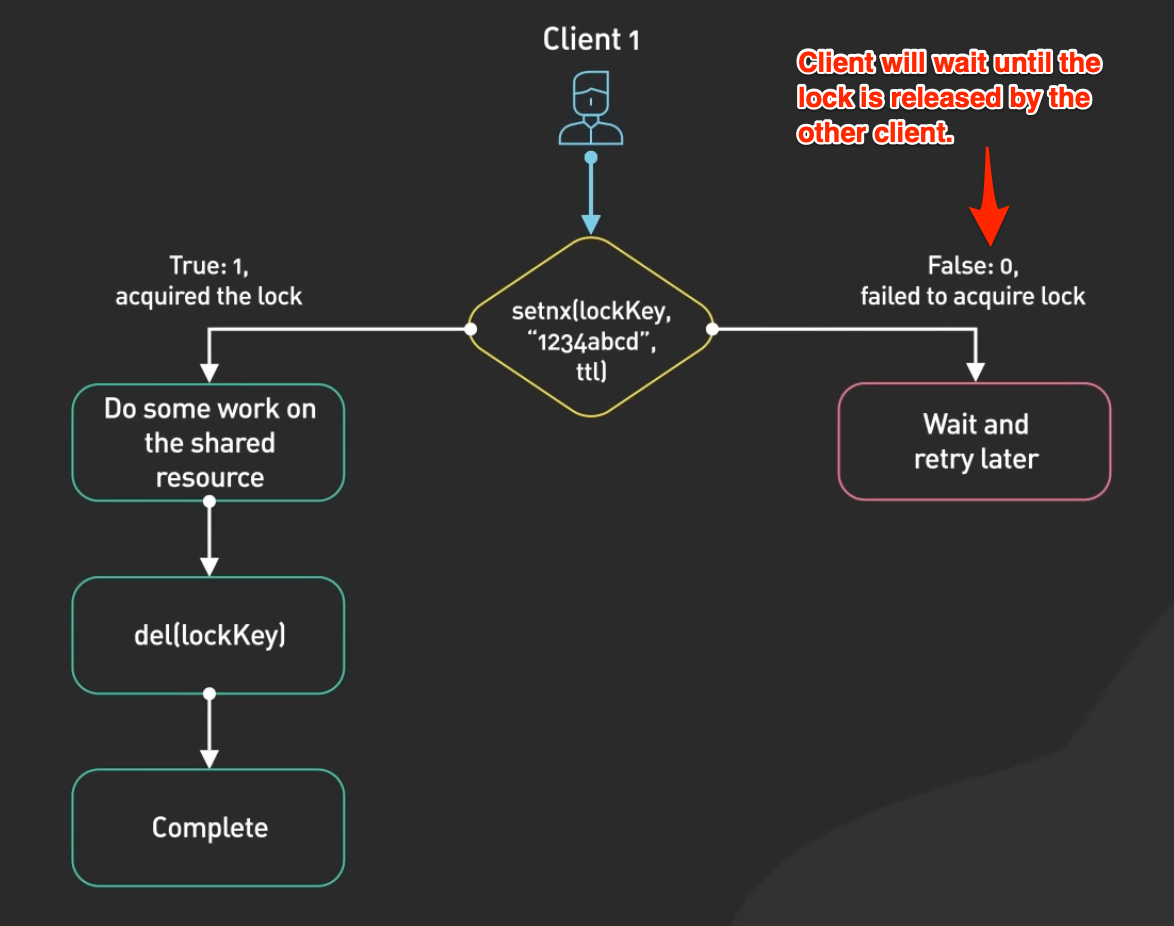
For production use, there are many Redis client libraries that provide high quality distributed lock implementation built out of the box.
- Redlock-py
- Pottery
- Aioredlock
- Redlock-php
- PHPReedisMutex
- chepresov/php-redis-lock
- rtckit/react-redlock
- Redsync
- Redisson
- Redis::DistLock
- Redlock-cpp
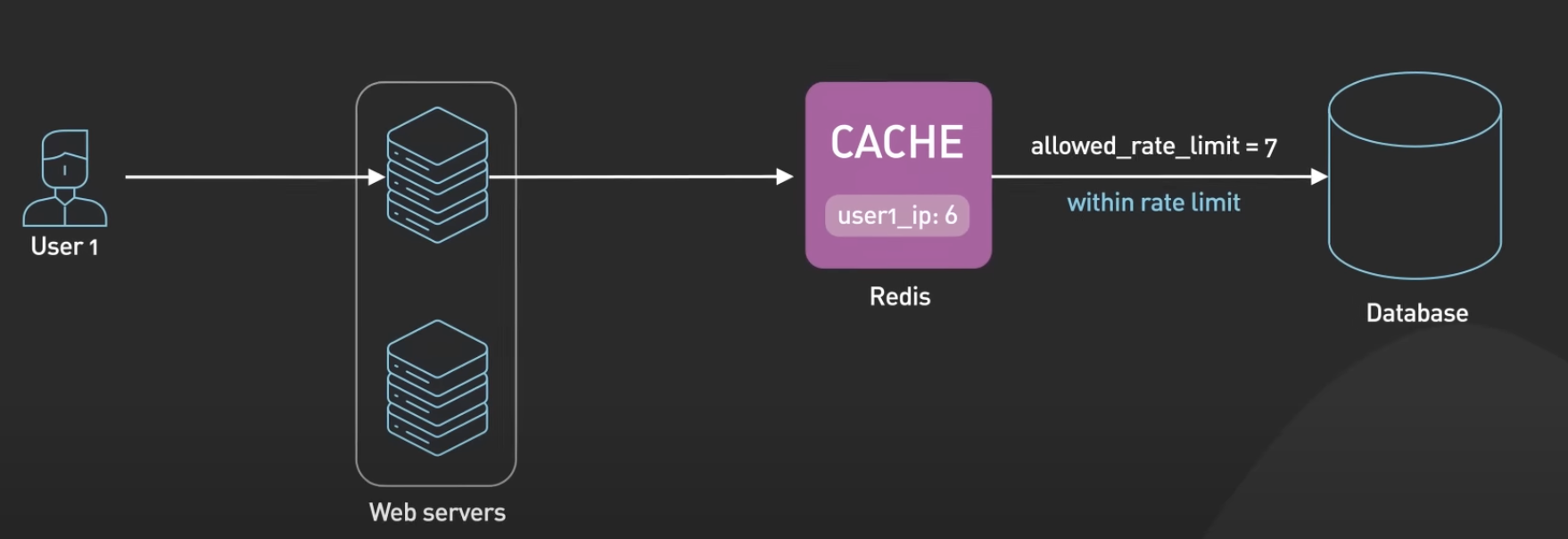
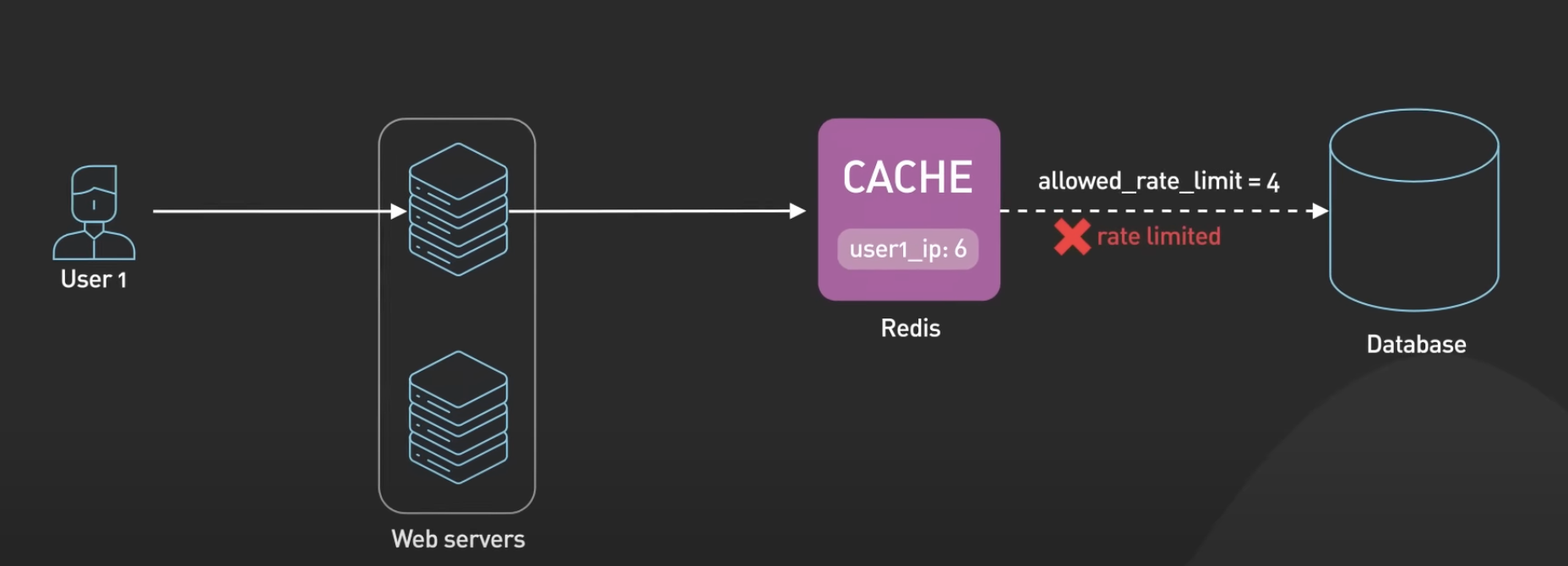
Rate Limiter
Redis can be used as a rate limiter by using its increment command on some counters and setting expiration times on those counters.
A basic example would be incrementing a value for a key using the INCR command. The current count would be compared to
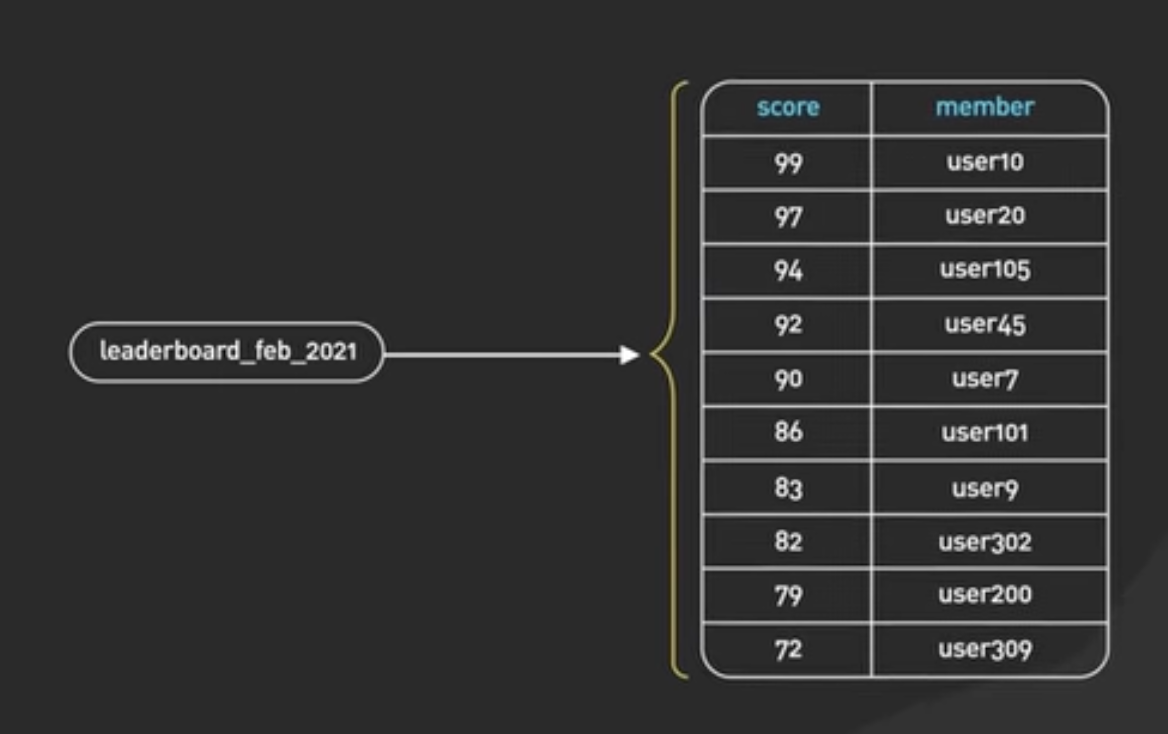
Ranking/Leaderboard
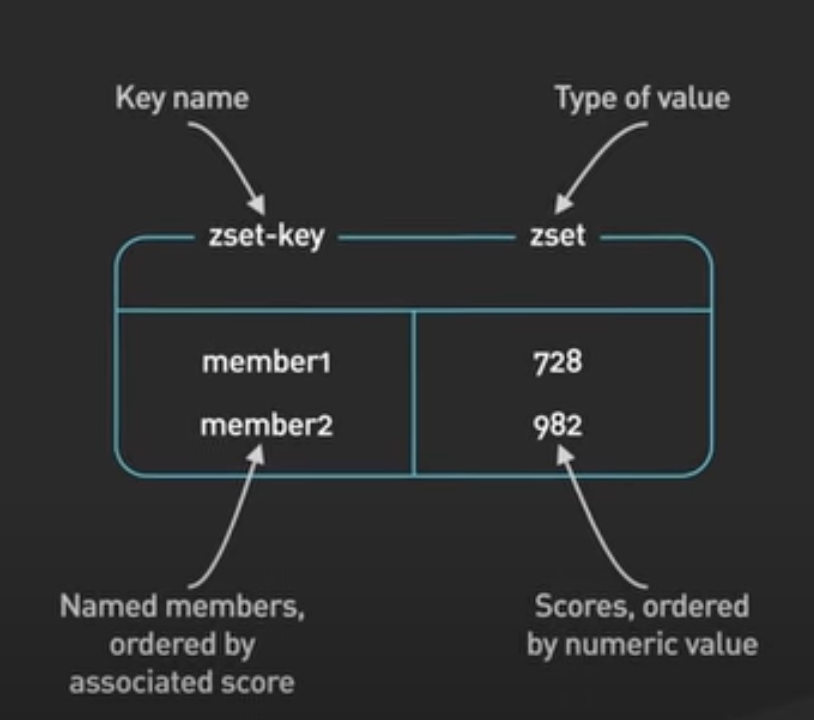
…sorted sets are the fundamental data structuctures that enable [ranking/leaderboards]
A sorted set is a collection of unique elements, each with a score associated with it.
The elements are sorted by score. This allows for quick retrieval of the elements by score in logarithmic time.